The final stage
Let us bring your model to a physical form
3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a groundbreaking
technology that has transformed the traditional approach to creating objects.
Instead of subtracting material from a larger piece
as in traditional manufacturing), 3D printing builds objects layer by layer
from digital models. This process allows for incredible design flexibility,
enabling the production of intricate and complex shapes that would be
challenging or impossible with conventional methods.
One of the key advantages of 3D printing is its versatility across various
industries. In product development and prototyping, designers can quickly
iterate and test ideas, accelerating the innovation cycle. In healthcare,
3D printing is used to create custom implants, prosthetics, and even organs.
The aerospace industry benefits from lightweight and precisely engineered
components, while architects and artists explore new possibilities in creating
unique structures and sculptures. The adaptability of 3D printing continues to
open up new avenues for creativity and problem-solving.
As the technology advances, the range of materials used in 3D printing expands.
From traditional thermoplastics like PLA and ABS to advanced composites,
metals, and biocompatible resins, the material options cater to diverse
applications. This evolution underscores the transformative impact of 3D
printing on manufacturing processes, enabling more sustainable practices and
pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in design and production.
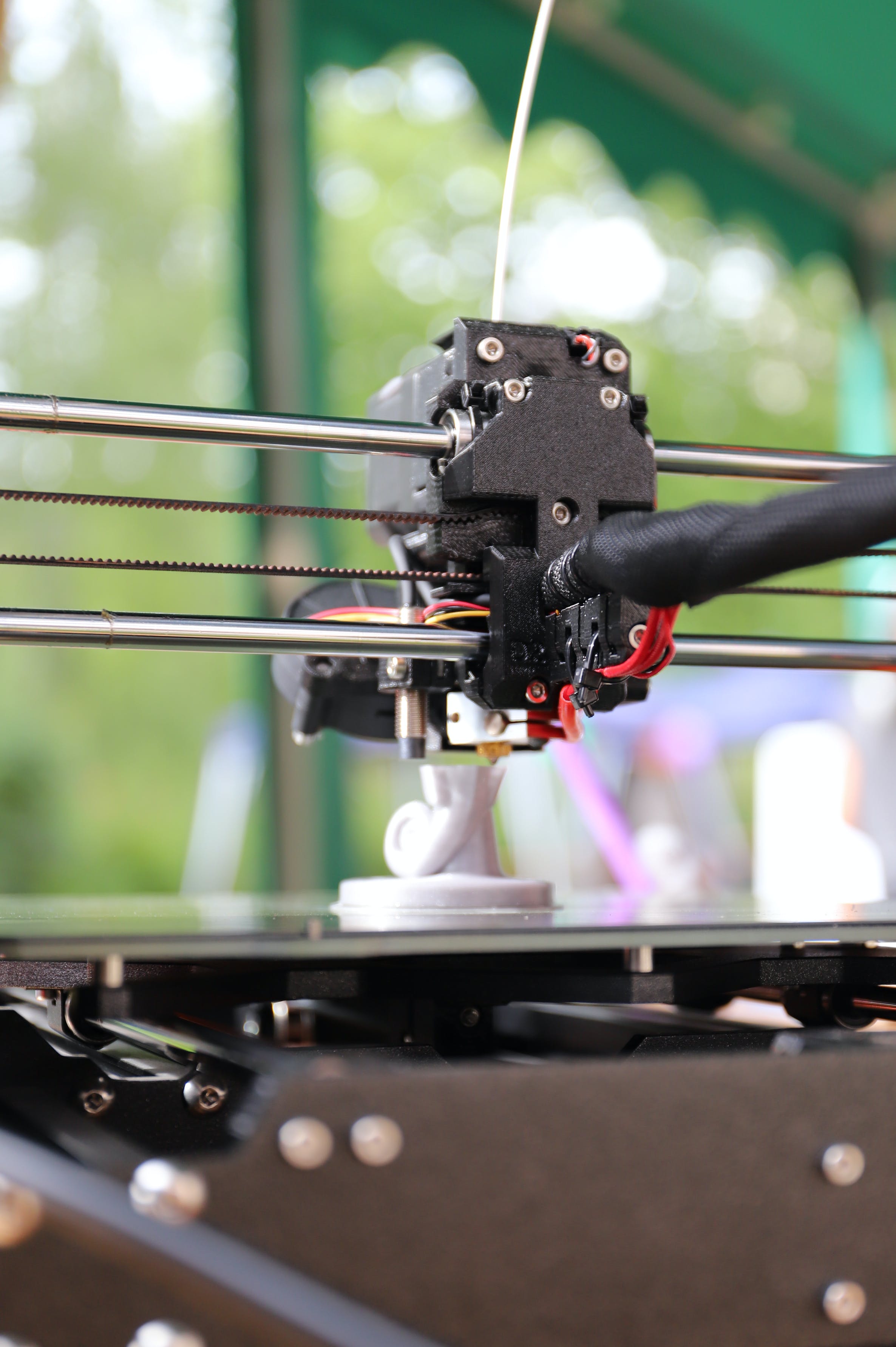
Printers
In our 3D printing services, we provide a couple of different options to
cater to your specific needs –
Fused Layer Modeling (FLM) and Masked Stereolithography (MSLA).
Each of these methods has its unique strengths, and the choice between
them depends on factors like the desired resolution and material
properties for your project. FLM, a commonly used method, involves
layering thermoplastic filaments to construct objects, offering
versatility in material choices such as PLA or ABS. On the other hand,
MSLA employs a liquid photopolymer resin cured by UV light,
providing high-resolution prints with smooth surfaces.
The decision on the appropriate printing method is a collaborative one, where we work closely with you to understand the specific requirements of your project. If intricate details and a smooth finish are crucial, MSLA might be the preferred choice. For applications requiring durability and a wide range of material options, FLM might be the optimal solution. This joint decision ensures that the selected 3D printing method aligns perfectly with your project goals, guaranteeing the best possible outcome in terms of both aesthetics and functionality.
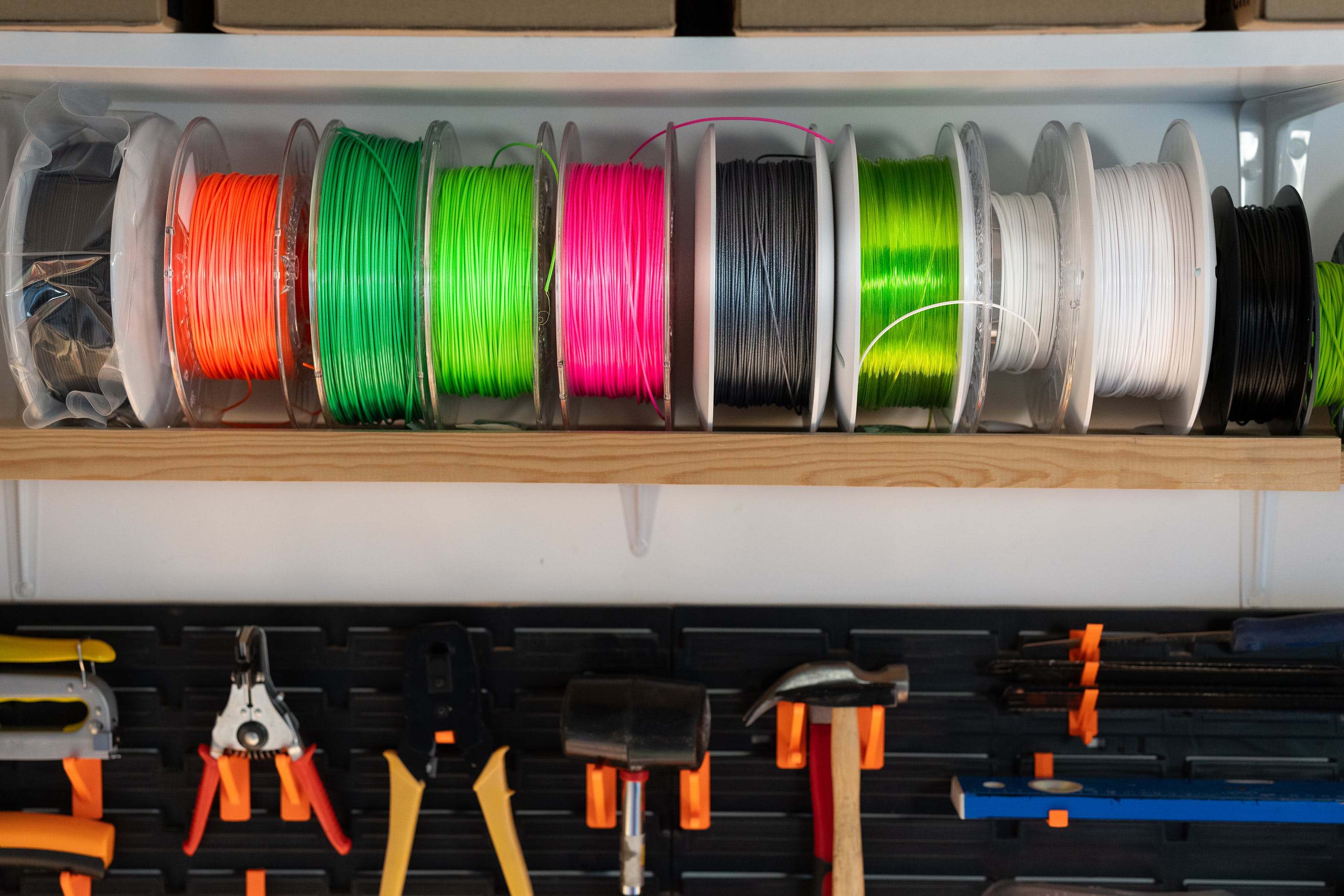

FLM - Filament
FLM (Fused Layer Modeling) is a widely used 3D printing filament type, commonly composed of thermoplastic materials such as PLA or ABS. FLM filaments are fed through the 3D printer's extruder, where they melt and are deposited layer by layer to create the desired object. This versatile filament is favored for its ease of use, affordability, and availability in various colors, making it suitable for a wide range of prototyping and manufacturing applications in the additive manufacturing field.

MSLA - Resin
MSLA (Masked Stereolithography) is a resin-based 3D printing technology that utilizes a liquid photopolymer resin as its filament counterpart. Unlike traditional Fused Layer Modeling (FLM) filaments, MSLA operates by selectively curing layers of resin using a UV light source. This results in high-resolution prints with smooth surfaces and intricate details. MSLA filaments come in liquid form and offer a diverse range of resin materials, including standard, flexible, and specialized resins for various applications, making it a preferred choice for intricate and detailed 3D prints.
